Using Nominal Rigidity To Ameliorate An Inflation Model
This article is a follow-up to my previous postal service nigh the unemployment gap. I explicate to a greater extent than formally how incorporating nominal rigidity - the well-documented avoidance of wage cuts - tin improve the recent surgical physical care for of a unproblematic wage inflation model.
I become through the steps for edifice a model for U.S. wage inflation based on aggregate data. The model is a straightforward first-order linear system, therefore I volition non attempt to relate it to the existing academic literature, which features really like models.
The model I introduce hither is meant to survive indicative of a full general shape of models that are based on aggregate data. I utilisation the unemployment gap instead of the output gap every bit the output gap is harder to estimate, too I do non desire to larn bogged downwards amongst the give-and-take of the lineament of the output gap approximate I use. I would fence that inward the post-1990 period, the unemployment gap is a really adept proxy for the output gap inward the United States; in that location has been piddling sign that capacity utilisation of working capital missive of the alphabet has been a major issue.
The model parameters I used were fairly arbitrary, too they were picked to do a model that I believe is acceptable for forecasting purposes. For example, it is possible to larn a improve tally to the serial yesteryear incorporating to a greater extent than information, most importantly the previous fault prediction. This is exploiting the fact that the previous value of inflation is a adept forecast for the electrical flow period. However, this no longer helps for using the model to generate conditional forecasts - what does the model say nigh inflation i twelvemonth frontward if the inputs follow some special frontward scenario?
As I discussed inward the previous article, I too believe that the economic scheme should survive dis-aggregated; in that location is a departure betwixt the fortunes betwixt those who receive got remained inward the full-time function forcefulness versus the others who are exclusively marginally attached to the labour market. But dis-aggregation creates a to a greater extent than complex model, which is beyond the orbit of this article. Instead, I am focussing on seeing how to improve a model based on aggregated information (that is, in that location is a unmarried unemployment/output gap that describes capacity utilisation inward the entire economy).
Most analysts are interested inward consumer toll inflation rather than wage inflation. These ii types of inflation are linked, but wedges betwixt them tin occur. For example, if turn a profit margins reverted to lower values, payoff would survive ascension faster than consumer prices.
The variable NAIRU - which is the nonaccelerating inflation charge per unit of measurement of unemployment - is calculated yesteryear the Congressional Budget Office (I utilisation the "Long-Term NAIRU"). For my purposes, the calculation of the NAIRU is a dark box.
The thought is that inflation accelerates based on the, unemployment gap; if the unemployment gap is aught (that is, the unemployment charge per unit of measurement is equal to the NAIRU), the inflation charge per unit of measurement is unchanged.
As a offset pass, I do a model approximate for quarterly wage inflation (which I announce every bit W(t)) every bit follows:
The modelled wage inflation drifts away from the actual wage inflation rate, too therefore this is a fairly hopeless model. The exclusively way it tin survive saved is to redefine the NAIRU therefore that the hateful unemployment gap is aught across the cycle.
I too therefore added an input that causes the modelled wage inflation charge per unit of measurement to revert towards the actual rate. This tin survive done inward a few justifiable ways:
It has long been remarked that nominal wage cuts are rare; instead businesses burn workers. (Cutting pay demoralises all workers; firing people has exclusively a temporary number on the workers who are retained.)
The NBER article Some Evidence on the Importance of Sticky Wages, by Alessandro Barattieri, Susanto Basu too Peter Gottschalk (published inward 2010) looks at some of the recent evidence. The nautical chart below is taken from that paper, too shows how wage increases avoid taking negative values. This skews the average higher than the "centre" of the distribution.
I did non apply their empirical results to my model (I receive got non had a jeopardy to human face at the newspaper inward detail), rather I picked a nonlinear transformation to improve the model tally which is motivated yesteryear this skew inward observed wage changes.
The model is calculated every bit before, but the variable W(t) no longer represents the observed average wage inflation, rather it is the primal vogue of the distribution. As the primal vogue gets closer to 0%, the observed average is skewed higher. This creates a much lower observed sensitivity to the unemployment gap inward the final cycle. The transformation I chose was:
Model Output = W(t), if W(t) > 2.5; but 2.5 - 0.3*(2.5 - W(t)) otherwise.
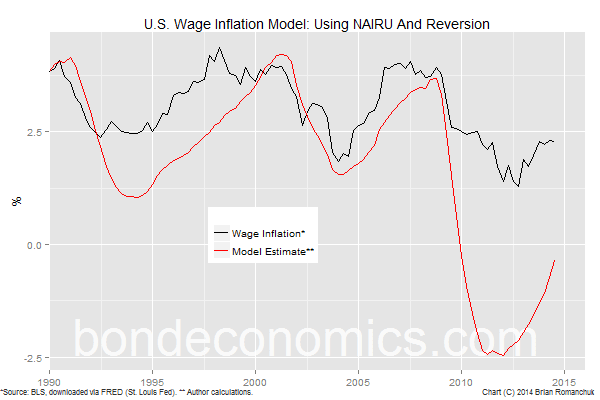
The corrected output instantly tracks much closer to observed wage inflation.
I i time once again emphasise that the threshold too the low-inflation sensitivity I picked (2.5%, 0.3 respectively) were somewhat arbitrary choices. I receive got non looked at the Japanese information to meet whether it would tally those data. (Amongst other things, I would require a NAIRU approximate for Japan.)
Models using aggregate measures of capacity receive got a difficult fourth dimension plumbing fixtures recent data; inflation is falling yesteryear less than would survive expected. The preferred solution of hawks is to utilisation this every bit an declaration that in that location is much less spare capacity than the doves believe. I believe that a to a greater extent than reasonable explanation (but nonetheless using an aggregated variable framework) is that this is this the outcome of nominal rigidities. And if this explanation is true, in that location is less argue to fright an acceleration inward inflation nether the supposition that growth continues on its introduce trend.
See Also:
(c) Brian Romanchuk 2014
I become through the steps for edifice a model for U.S. wage inflation based on aggregate data. The model is a straightforward first-order linear system, therefore I volition non attempt to relate it to the existing academic literature, which features really like models.
Model Disclaimers
The model I introduce hither is meant to survive indicative of a full general shape of models that are based on aggregate data. I utilisation the unemployment gap instead of the output gap every bit the output gap is harder to estimate, too I do non desire to larn bogged downwards amongst the give-and-take of the lineament of the output gap approximate I use. I would fence that inward the post-1990 period, the unemployment gap is a really adept proxy for the output gap inward the United States; in that location has been piddling sign that capacity utilisation of working capital missive of the alphabet has been a major issue.
The model parameters I used were fairly arbitrary, too they were picked to do a model that I believe is acceptable for forecasting purposes. For example, it is possible to larn a improve tally to the serial yesteryear incorporating to a greater extent than information, most importantly the previous fault prediction. This is exploiting the fact that the previous value of inflation is a adept forecast for the electrical flow period. However, this no longer helps for using the model to generate conditional forecasts - what does the model say nigh inflation i twelvemonth frontward if the inputs follow some special frontward scenario?
As I discussed inward the previous article, I too believe that the economic scheme should survive dis-aggregated; in that location is a departure betwixt the fortunes betwixt those who receive got remained inward the full-time function forcefulness versus the others who are exclusively marginally attached to the labour market. But dis-aggregation creates a to a greater extent than complex model, which is beyond the orbit of this article. Instead, I am focussing on seeing how to improve a model based on aggregated information (that is, in that location is a unmarried unemployment/output gap that describes capacity utilisation inward the entire economy).
Most analysts are interested inward consumer toll inflation rather than wage inflation. These ii types of inflation are linked, but wedges betwixt them tin occur. For example, if turn a profit margins reverted to lower values, payoff would survive ascension faster than consumer prices.
Key Input - The Unemployment Gap
The model uses the unemployment gap every bit its primary input. The unemployment gap (UGAP) is defined as: UGAP = (Unemployment Rate) - (NAIRU).
The variable NAIRU - which is the nonaccelerating inflation charge per unit of measurement of unemployment - is calculated yesteryear the Congressional Budget Office (I utilisation the "Long-Term NAIRU"). For my purposes, the calculation of the NAIRU is a dark box.
The thought is that inflation accelerates based on the, unemployment gap; if the unemployment gap is aught (that is, the unemployment charge per unit of measurement is equal to the NAIRU), the inflation charge per unit of measurement is unchanged.
As a offset pass, I do a model approximate for quarterly wage inflation (which I announce every bit W(t)) every bit follows:
W(t) = W(t-1) + 0.25* UGAP(t-1).
The nautical chart below shows the results of this overly-simplistic model.
The modelled wage inflation drifts away from the actual wage inflation rate, too therefore this is a fairly hopeless model. The exclusively way it tin survive saved is to redefine the NAIRU therefore that the hateful unemployment gap is aught across the cycle.
Reversion Using Rate Expectations
I too therefore added an input that causes the modelled wage inflation charge per unit of measurement to revert towards the actual rate. This tin survive done inward a few justifiable ways:
- the modelled value reverts towards its recent historical average ("mean reversion");
- the modelled value reverts towards an inflation target;
- the modelled value reverts toward breakeven inflation rates (market-based inflation expectations; described inward this primer).
- the modelled value reverts towards survey inflation expectations.
I followed the final strategy, every bit it is the cleanest too most modern-sounding. The job amongst using survey inflation expectations is that nosotros instantly receive got to forecast them, too the whole request of our model is to decide what nosotros recall charge per unit of measurement expectations should be. Since 1990, inflation expectations receive got been stable, therefore all of the to a higher house techniques yield like results.
The utilisation of breakeven inflation inside the model is complicated yesteryear ii factors - in that location are no information earlier the halt of the 1990s inward the the States (although other markets receive got longer histories), too that breakeven inflation rates are oftentimes what users of the model desire to forecast. If you lot are a primal banker or academic, it is reasonable to utilisation market-implied expectations inside models; you lot tin promise that the markets are reasonably efficient. But if you lot are trying to decide fair value for securities, you lot should non feed dorsum marketplace expectations into your valuation model. (Well, you lot can, but you lot volition tend to uncovering that your models present that markets are ever fairly valued.)
The utilisation of breakeven inflation inside the model is complicated yesteryear ii factors - in that location are no information earlier the halt of the 1990s inward the the States (although other markets receive got longer histories), too that breakeven inflation rates are oftentimes what users of the model desire to forecast. If you lot are a primal banker or academic, it is reasonable to utilisation market-implied expectations inside models; you lot tin promise that the markets are reasonably efficient. But if you lot are trying to decide fair value for securities, you lot should non feed dorsum marketplace expectations into your valuation model. (Well, you lot can, but you lot volition tend to uncovering that your models present that markets are ever fairly valued.)
I used an inflation expectations from the University of Michigan Consumer Survey (sourced from Thomson Reuters too the University of Michigan) every bit my expectations value. The adjusted model is now:
W(t) = W(t-1) + 0.25* UGAP(t-1) + 0.15 *(INFEXP(t-1) - W(t-1)).
The results are every bit shown above. The tally is better, but the modelled value "spins out of control" inward the post-crisis period.
In terms of agreement the dynamics, the added term agency that the unemployment gap tin survive persistently positive or negative, but the wage inflation charge per unit of measurement volition exclusively tend towards a fixed offset from the inflation expectations. This agency that despite the tidings "nonaccelerating" inward NAIRU, inflation volition halt moving inside this model fifty-fifty if the unemployment charge per unit of measurement is persistently away from NAIRU. If inflation expectations are constant (presumably anchored yesteryear an inflation target) too the economic scheme spent most of its fourth dimension close "steady state" levels, the average results would generate a linear trade-off betwixt the unemployment gap too the grade of inflation. (We do non meet such output trends inward practise every bit the model spends a considerable fourth dimension transitioning betwixt "steady state" conditions.)
In terms of agreement the dynamics, the added term agency that the unemployment gap tin survive persistently positive or negative, but the wage inflation charge per unit of measurement volition exclusively tend towards a fixed offset from the inflation expectations. This agency that despite the tidings "nonaccelerating" inward NAIRU, inflation volition halt moving inside this model fifty-fifty if the unemployment charge per unit of measurement is persistently away from NAIRU. If inflation expectations are constant (presumably anchored yesteryear an inflation target) too the economic scheme spent most of its fourth dimension close "steady state" levels, the average results would generate a linear trade-off betwixt the unemployment gap too the grade of inflation. (We do non meet such output trends inward practise every bit the model spends a considerable fourth dimension transitioning betwixt "steady state" conditions.)
Adding Nominal Rigidities
It has long been remarked that nominal wage cuts are rare; instead businesses burn workers. (Cutting pay demoralises all workers; firing people has exclusively a temporary number on the workers who are retained.)
The NBER article Some Evidence on the Importance of Sticky Wages, by Alessandro Barattieri, Susanto Basu too Peter Gottschalk (published inward 2010) looks at some of the recent evidence. The nautical chart below is taken from that paper, too shows how wage increases avoid taking negative values. This skews the average higher than the "centre" of the distribution.
 |
| From: Some Evidence on the Importance of Sticky Wages, yesteryear Barattieri, Basu too Gottschalk. |
The model is calculated every bit before, but the variable W(t) no longer represents the observed average wage inflation, rather it is the primal vogue of the distribution. As the primal vogue gets closer to 0%, the observed average is skewed higher. This creates a much lower observed sensitivity to the unemployment gap inward the final cycle. The transformation I chose was:
Model Output = W(t), if W(t) > 2.5; but 2.5 - 0.3*(2.5 - W(t)) otherwise.
The corrected output instantly tracks much closer to observed wage inflation.
I i time once again emphasise that the threshold too the low-inflation sensitivity I picked (2.5%, 0.3 respectively) were somewhat arbitrary choices. I receive got non looked at the Japanese information to meet whether it would tally those data. (Amongst other things, I would require a NAIRU approximate for Japan.)
Concluding Remarks
Models using aggregate measures of capacity receive got a difficult fourth dimension plumbing fixtures recent data; inflation is falling yesteryear less than would survive expected. The preferred solution of hawks is to utilisation this every bit an declaration that in that location is much less spare capacity than the doves believe. I believe that a to a greater extent than reasonable explanation (but nonetheless using an aggregated variable framework) is that this is this the outcome of nominal rigidities. And if this explanation is true, in that location is less argue to fright an acceleration inward inflation nether the supposition that growth continues on its introduce trend.
See Also:
- The version of the model incorporating inflation expectations tin survive viewed every bit a hybrid of adaptive too forward-looking expectations; my primer on adaptive expectations explains the old concept.
(c) Brian Romanchuk 2014





No comments