The Race To Enhance Involvement Rates
If y'all practice non similar the sporting metaphors inwards the postal service below, y'all tin give notice blame novel MPC fellow member Andy Haldane whose speech I receive got simply read. Or maybe the World Cup.
When it comes to monetary policy, inwards recent years the U.K. has consistently followed the US. The U.S. Fed started reducing involvement rates inwards September 2007, too hitting the Zero Lower Bound (ZLB) at the terminate of 2008. The UK’s MPC started reducing involvement rates inwards Oct 2008, too hitting the ZLB inwards March 2009. The lag betwixt the 2 shortened considerably with Quantitative Easing, which the U.K. started simply 2 months afterwards the US. The MPC likewise followed the Fed with forwards guidance, using a rattling similar formula.
The large query today for monetary policy inwards both the U.S. too U.K. is when involvement rates volition start to increase. Until rattling lately this looked similar a race that neither fundamental banking concern was keen to enter, at to the lowest degree for a while. But that all changed lastly week next a spoken language past times U.K. Governor Mark Carney. That led Gavyn Davies to around the same level every bit it was inwards Jan 2008, piece U.S. output is over 6% higher upward its pre-recession peak. This would usually imply that the U.K. should live next good behind the U.S. inwards raising rates.
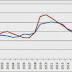
What virtually the labour market? Here is a nautical chart comparison unemployment inwards both countries.
I receive got taken the OECD’s latest Economic Outlook forecast for the US, but I receive got used much to a greater extent than optimistic numbers for the UK: 6.4% for 2014, too 5.7% for 2015. (Unemployment inwards May was 6.6%.) It is truthful that for unemployment, the lag betwixt the U.K. recovery too the U.S. recovery is shorter than for gross domestic product growth. However they seem to live inwards similar territory at the moment, with unemployment unlikely to render to 2000-2007 numbers past times 2015. In addition, at that spot may live to a greater extent than labour marketplace slack than is implied past times these numbers, although for different reasons inwards each country. One lastly quest worth are stagnant, too wage growth inwards the U.K. continues to live below cost inflation. In the UK, at that spot is fifty-fifty closed to dubiety whether rising existent payoff would set that much upward describe per unit of measurement area on cost inflation. Some purpose of the U.K. productivity puzzle must be the resultant of component subdivision substitution: using labour rather than machines because existent payoff are depression relative to the cost of capital. If that is the case, at that spot is orbit to opposite this if existent payoff start to rise, pregnant that wage increases are non fully passed on into prices.
One surface area which is oftentimes talked virtually where the U.K. is good ahead is the housing market, with U.K. prices rising rapidly. House prices are non purpose of the consumer prices index, but closed to fence that they should be. This is problematic conceptually - rents are the cost of housing services, too solid prices are the cost of an asset. As I pointed out here, what nosotros receive got inwards the U.K. at the instant is a ascension inwards solid prices relative to rents, which may inwards plow reverberate the combination of falling involvement rates too static supply, plus mayhap a fleck of froth on top. According to the ONS data, rents receive got non been rising apace since the recession.
As John Williams alongside many others receive got emphasised, using involvement rates to calm the housing marketplace when inflation is below target has proved disastrous for Sweden too Norway. Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 housing nail is non a reliable indicator of incipient inflation. The U.K. should surely non follow the Scandinavian illustration inwards this item respect.
Taking all this together, who volition live the showtime to enhance rates? My feeling is that U.S. monetary policy makers are on reasonably solid ground, too are not even inwards their starting blocks. The output gap inwards the U.S. is sufficiently large that at that spot is picayune postulate to start raising rates now. U.K. monetary policy makers are inwards a much to a greater extent than hard place, because of the U.K. productivity puzzle. The Carney spoken language has inwards outcome tightened monetary policy past times appreciating the telephone exchange rate, every bit he must receive got known it would. Before this I had hoped that they would at to the lowest degree hold back until existent payoff started rising significantly, but straight off I’m less sure. I fright afterwards the Carney spoken language that they receive got entered the starting blocks, too whatever dissonance mightiness trigger a faux start.
The job for the U.K. is that the strategy of wanting to start raising rates earlier inflation exceeds the target is inappropriate given the extreme uncertainties implied past times the productivity puzzle. As Mark Thoma before, the risks are non symmetric. It would live unfortunate if inflation started rising earlier involvement rates started increasing, but the costs of a few years of excess inflation would non live that great. The MPC has afterwards all been at that spot recently, too the the world did non come upward to an end. The costs of prematurely choking off a recovery are much greater when recent productivity too output losses mightiness live recoverable (as they were inwards the early on 1980s too 1990s). These are rattling potent grounds for the Bank of England to popular off along to follow the U.S. Fed, too non boundary the gun.
Postscript: Tony Yates elaborates on this lastly point, too likewise has to a greater extent than on the Haldane speech.


No comments